NeRFS (Neural Radiant Fields)
With NeRFS, the scene is encoded in a neural network.
Importantly, NeRFS still calculate the fundamental matrix, since the camera position needs to be known.
Volumetric Rendering
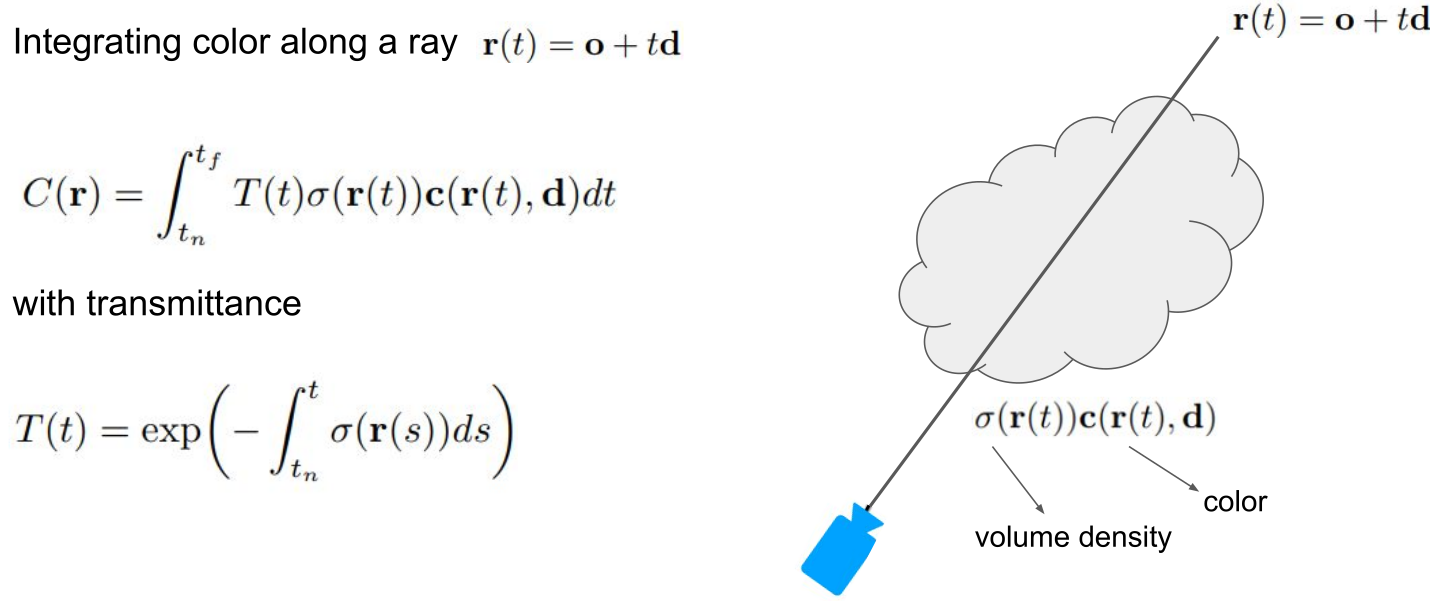
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JuH79E8rdKc&t=9
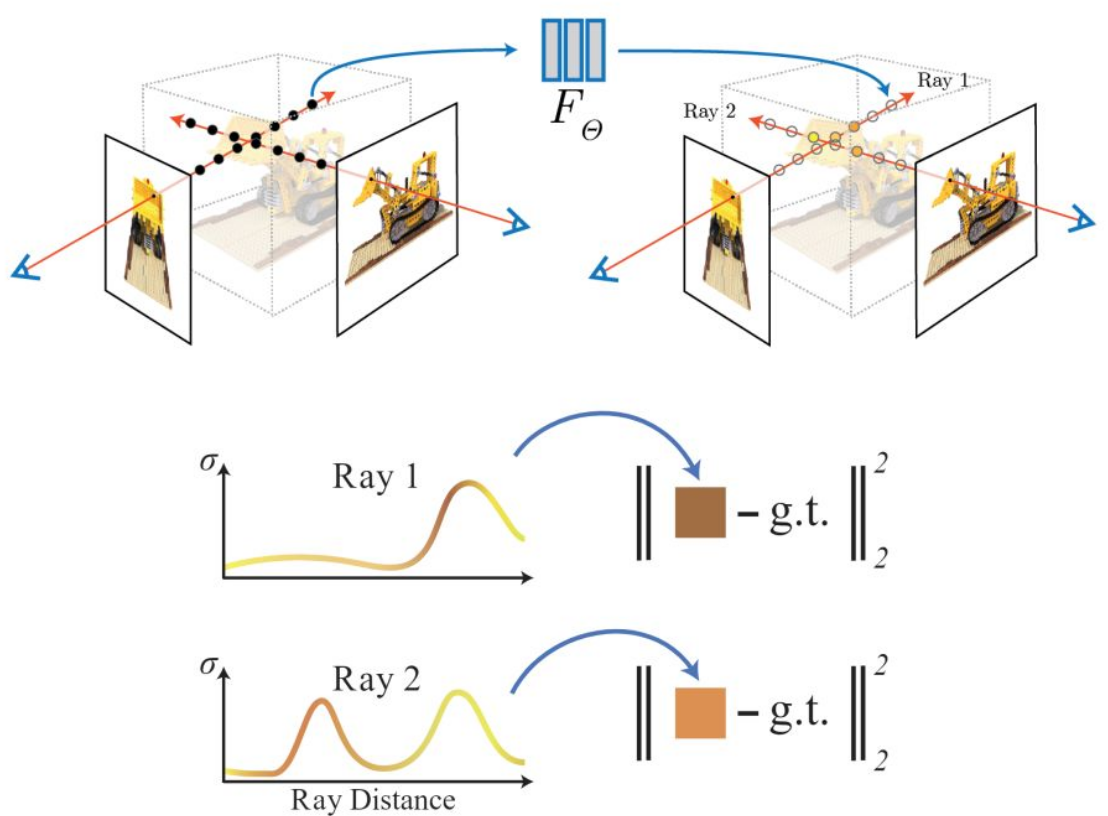
At each point on the line, the neural network is sampled. All of these points are averaged together.
To train the neural network, the loss function is defined as the difference between the averaged coloured and the actual colour.
One advantage is, that such a model can model things like highlights of a material or the transparency of a material. In the previous methods, each point could only have one colour.
A disadvantage of NeRF is that is really slow and doesn't handle unconstrained views well.
A NeRFS neural network should be overfitted, since it should not generalise to other viewes, but return the same views again.
A NeRFS neural network should be overfitted, since it should not generalise to other viewes, but return the same views again.
Gaussian Splats
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VkIJbpdTujE&t=80
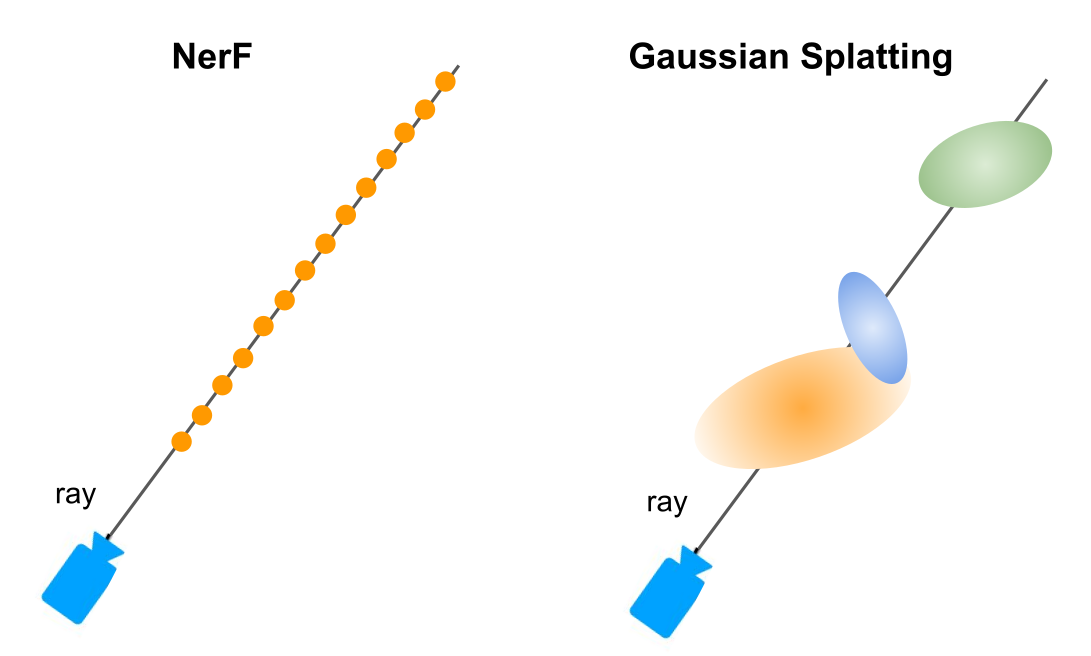
In comparison to NeRFs, gaussian splatting uses a eliphtical shape instead of dots. This has the advantage that we know how to render this with our current technology stack fast.
Initially, a point cloud is taken and each point is diffused into an ellipsoid. This marks the initial model. Then, gradient descent is used to optimise the the model.