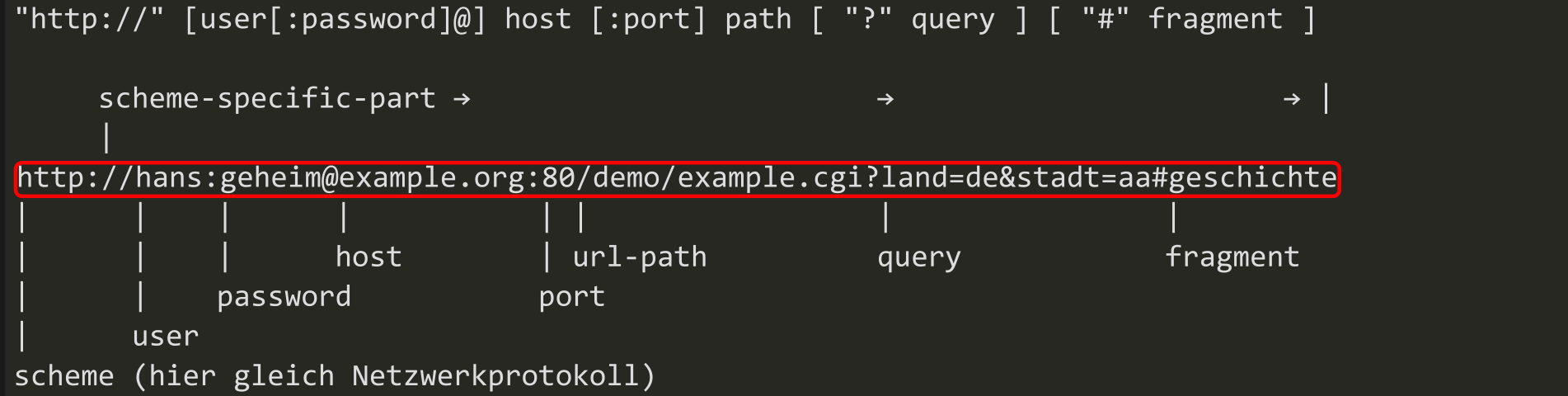
Express
HTTP Request Methods
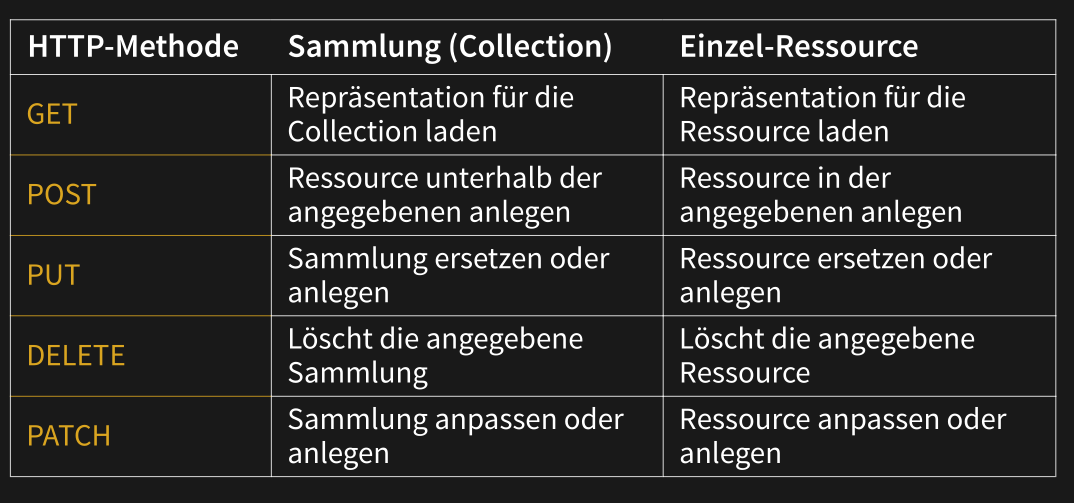
GET: Retrieve resourcePOST: Create a new resourcePUT: Update an already existing resourcePATCH: Partly update an already existing resource (e.g. only sending the first name if only this field is modified)DELETE: Delete a resource
Simple HTTP Server & Client
The simple server:
const {createServer} = require("http")
let server = createServer((request, response) => {
response.writeHead(200, {"Content-Type": "text/html"})
response.write(`
<h1>Hello!</h1>
<p>You asked for <code>${request.url}</code></p>`)
response.end()
})
server.listen(8000)
console.log("Listening! (port 8000)")
And the client:
const {request} = require("http")
let requestStream = request({
hostname: "eloquentjavascript.net",
path: "/20_node.html",
method: "GET",
headers: {Accept: "text/html"}
}, response => {
console.log("Server responded with status code", response.statusCode)
}
)
requestStream.end()
Post and Get Requests
The following code extracts get requests
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const port = 3000
app.post('/shoes', function (req, res, next) {
// GET /shoes?order=desc&shoe[color]=blue&shoe[type]=converse
console.dir(req.query.order)
// => 'desc'
console.dir(req.query.shoe.color)
// => 'blue'
console.dir(req.params.name)
}
app.post('/user/:name', function (req, res, next) {
// GET /user/tj
console.dir(req.params.name)
// => 'tj'
})
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening at http://localhost:${port}`)
})
The following code extracts post requests:
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const port = 3000
// for parsing application/json
app.use(express.json())
// for parsing application/x-www-form-urlencoded
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }))
app.post('/profile', function (req, res, next) {
console.log(req.body)
res.json(req.body)
})
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening at http://localhost:${port}`)
})
To serve static content the express.static middleware can be used:
app.use(express.static('public'))
// http://localhost:3000/css/style.css
// Pfad zur Datei: public/css/style.css
app.use('/static', express.static('public'))
// http://localhost:3000/static/css/style.css
// Pfad zur Datei: public/css/style.css
Middle Ware
Express is a sequence of middle wares. Some do error handling, some handle the actual request. Middle wares can also forward information to the next middle ware.
app.use(function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Time:', Date.now())
req.currentTime = Date.now()
next()
})
app.use('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
console.log("Time: ", req.currentTime)
console.log('Request Type:', req.method)
next()
})
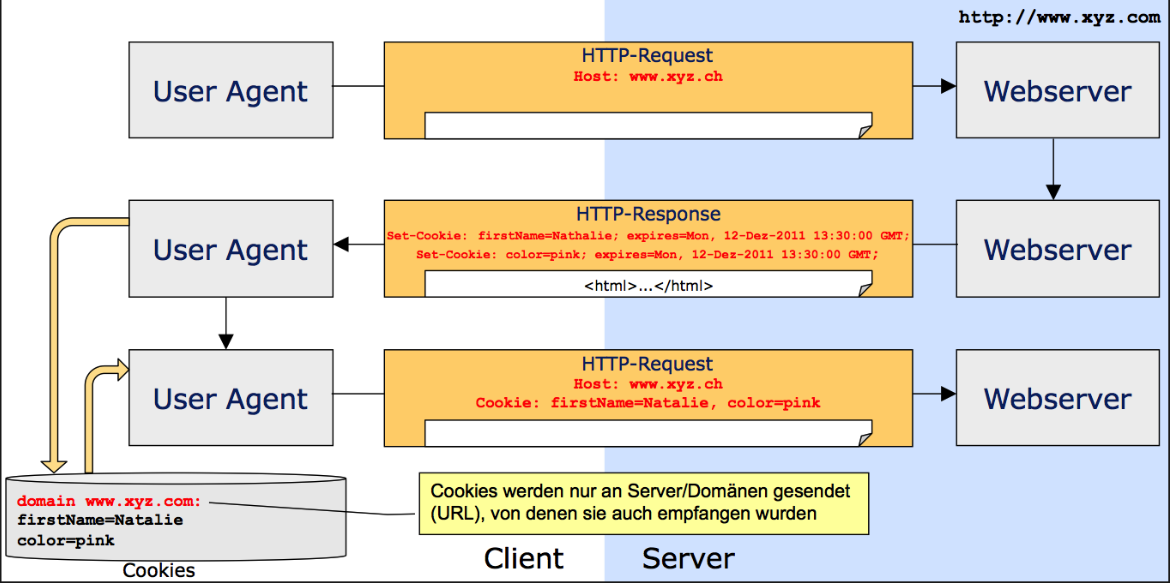
Cookies
Designed as a stateless protocol to store data on the browser. It can be set with the Set-Cookie header and can be read from JS (except if HttpOnly is set) with document.cookie. The client will send the cookie back with the Cookie Header.
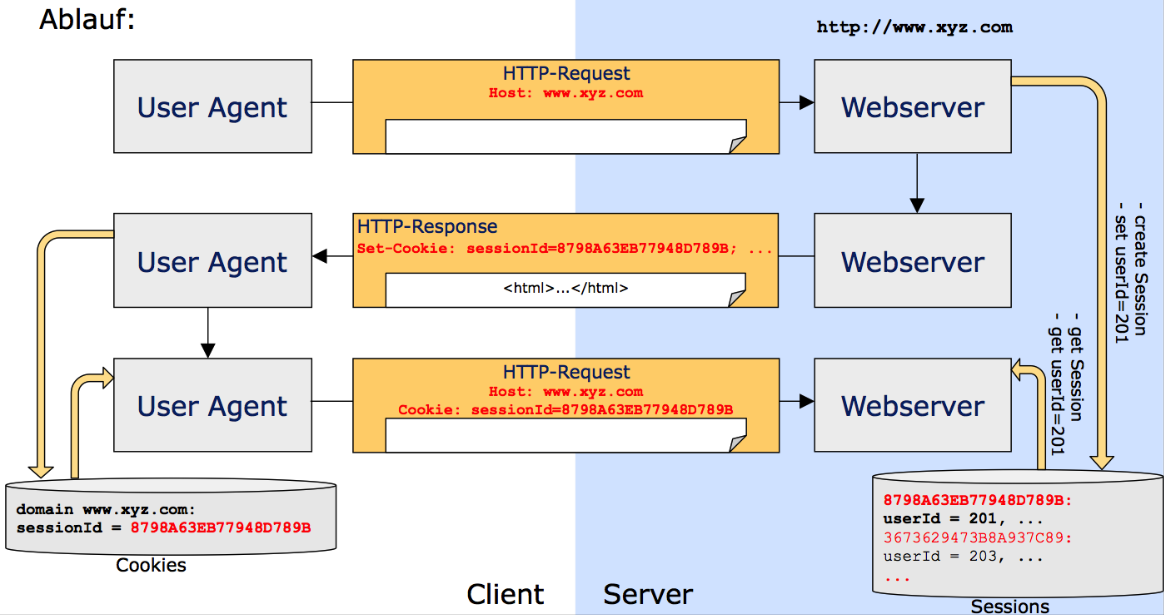
Sessions
Sessions can be realised with cookies, but sessions can be hijacked when the session id can be stolen (e.g. when using http)
// "npm install express-session" to install the express-session package
var express = require('express')
var cookieParser = require('cookie-parser')
var session = require('express-session')
var app = express();
app.use(cookieParser())
app.use(session({secret: "Shh, its a secret!"}))
app.get('/', function(req, res){
if(req.session.page_views){
req.session.page_views++
res.send("You visited this page " + req.session.page_views + " times")
} else {
req.session.page_views = 1
res.send("Welcome to this page for the first time!")
}
})
app.listen(3000)