VR
VR is a computer simulation to generate a realistic 3D virtual world. Therefore interactivity, immersion and presence (it looks and behaves like the real deal) is important.
People employ the use of VR for:
- the real thing is too dangerous
- the real thing doesn't exist
- The simulated objective is difficult or expensive to train in real life (e.g. surgery)
- The simulated object is not accessible (e.g. virtual autopsy table)
The following senses contribute the most to the perception of a human:
- Sight 70% (Visual Interface)
- Hearing 20% (Auditory Interface)
- Smelling 5% (Olfactory Interface)
- Touching 4% (Haptics Interface)
- Taste (Gustatory Interface)
- Balance (Vestibular Interfaces)
- Body Awareness (Locomotion Interface)
- Temperature
- Pain
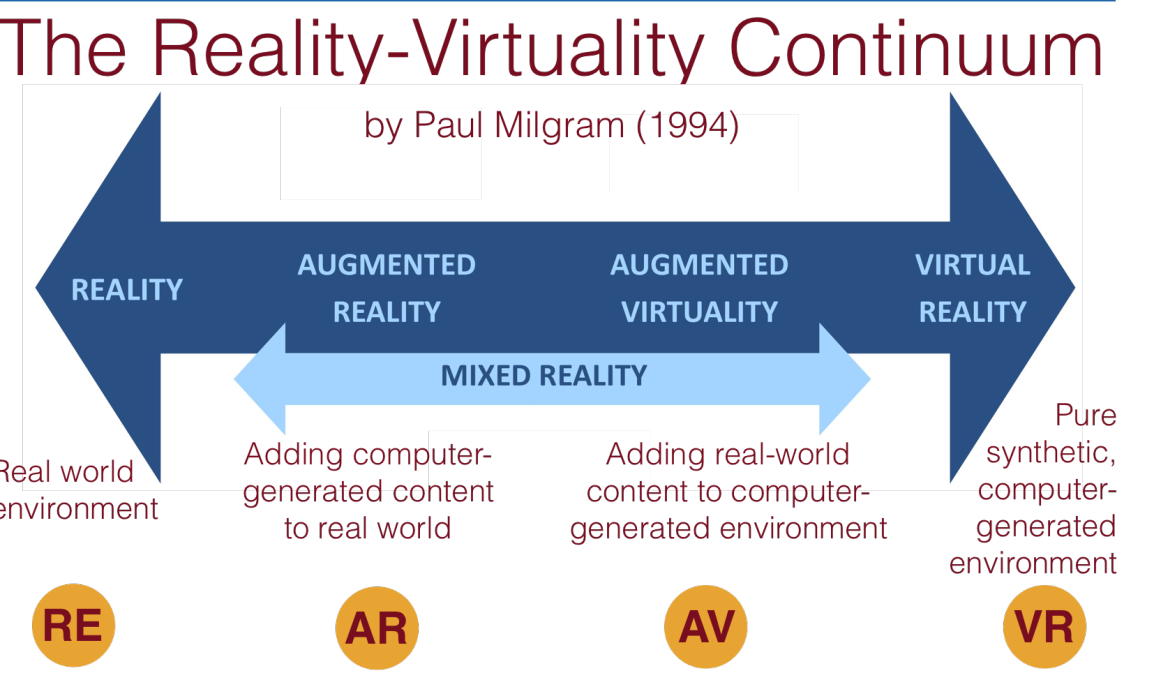
The Reality-Virtuality Continuum
Glossary
-
Physical Reality Resides in local, physical world (here and now)
-
Cyberspace A location that exists only in the mind of users and allows geographically distant people to interact with each other
-
Synthetic Environment = VR, AR, Telepresence
-
Telepresence Interact with a physically real, remote environment from the first person perspective
-
Teleoperation Remotely operate a device
Input
Fuse Buttons are one option of interactivity
Often time Motion Tracking is used. Alternatively, Gesture Recognition is implemented.
The body can be tracked with electromagnetic tracking .

More modern headsets use optical tracking.