Scanner
Fine Automaton (FA)
An FA is defined by the file-tuple \((S, A, T, s_0, S_F)\), where
- \(S\) is the set of states
- \(A\) is the alphabet
- \(T\) is a function that takes the current state and the current input character as an argument and returns another state
- \(s_0\in S\) is the start state
- \(S_F \in S\) the final state
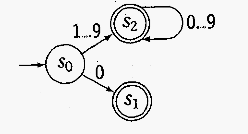
There is always an implicit error state, which the machine transitions to if there is no other valid state to transition into.
A DFA and NFA are equivalent. However, when converting a NFA into a DFA the state space can blow up exponentially.
Regex
- \(\varepsilon\) is a RE denoting the empty set
- \(x \mid y = L(x) \cup L(y)\) is an alternation and means \(x\) or \(y\)
- \(xy = L(x)L(y)\) is a concatenation
- \(x^*=L(x)^*\) is a closure and means zero or more \(x\)
The kleene closure is defined as \(L^* = \cup_{0\le i \le \infty}L^i\), while the positive closure is defined as \(L^+ = \cup_{1\le i \le \infty}L^i\)
The precedence is: closure, concatenation and then alteration.
Simple Scanner from a DFA
char <- NextChar()
state <- s0
while (char != eof)
state <- TransiationTable(state, char)
char <- NextChar()
if (state in finshStates)
ReportAcceptance()
else
ReportFailure()
Instead of this, scanners can also use labels and goto-statements to implement the scanner logic. While this is complex and difficult to debug, it is more permanent and good for automatically generated scanners.
Both a scanner based on a DFA or a RE need to continue consuming characters until the DFA reaches a final or error state or until the RE can't continue matching. Essentially, the longest possible match has to be found.
If the DFA stops at a non-final state, the DFA should report the last encountered final state or report an error.
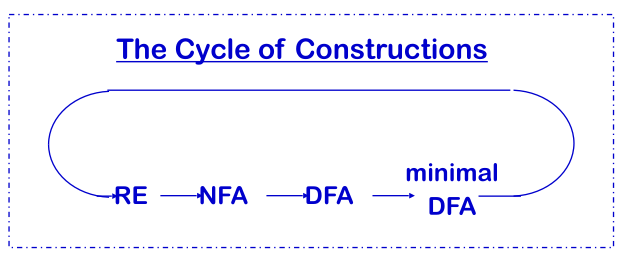
Cycle of Construction
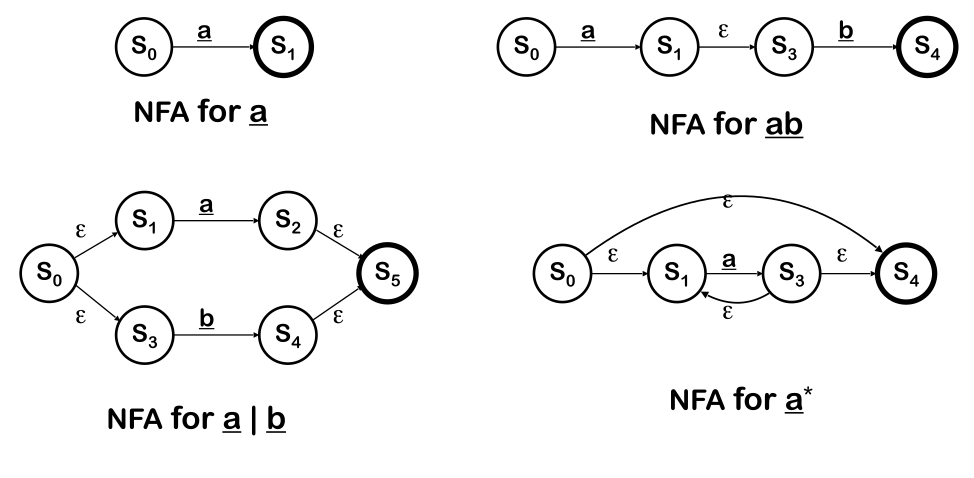
Thompson's Construction
To get from RE to a NFA, Thompson's construction can be used. It is based on the idea that two NFA's can be joined with \(\varepsilon\). For each operator and symbol, there is an NFA pattern, which are then joined.
Subset Construction
With the subset construction, one can convert an NFA into a DFA.
There are two key functions:
- \(Move(s_i, a)\) is the set of states reachable from \(s_i\) by consuming the character
a - \(\varepsilon-closure(s_i)\) is the set of states reachable from \(s_i\) by one or more \(\varepsilon\). \(s_i\) will always be part of the set.
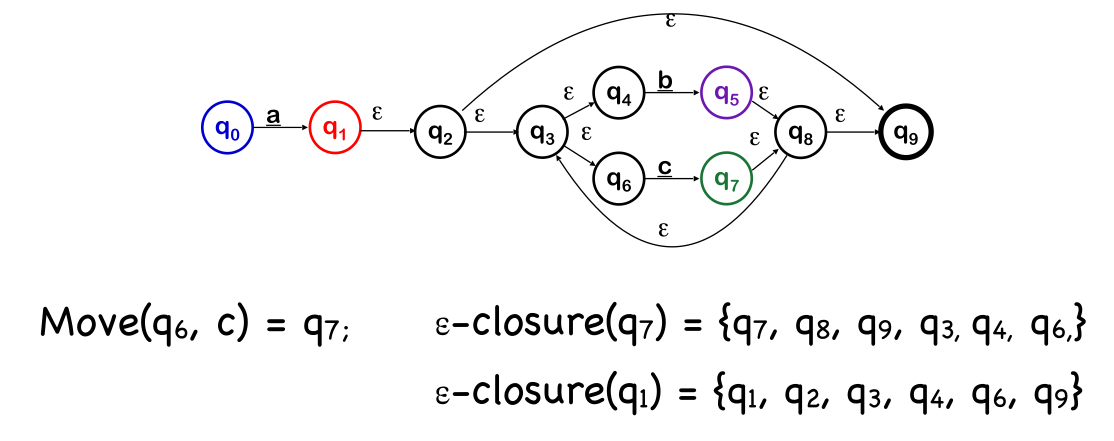
The algorithm does the following:
- Take the \(\varepsilon-closure(s_0)\) and add it to the DFA as the start state
- Take the \(\varepsilon cloure(Move(s_0, \alpha))\) for each \(\alpha \in \Sigma\) and add it to the DFA. Importantly, first only \(Move(s_i, \alpha)\) is considered (so only states directly reachable from \(s_i\)), and afterwards the \(\varepsilon closure(...)\) is calculated.
- Repeat 2. with the new states until no new states are added
- Mark all states which contain a final state of the NFA as final states of the DFA
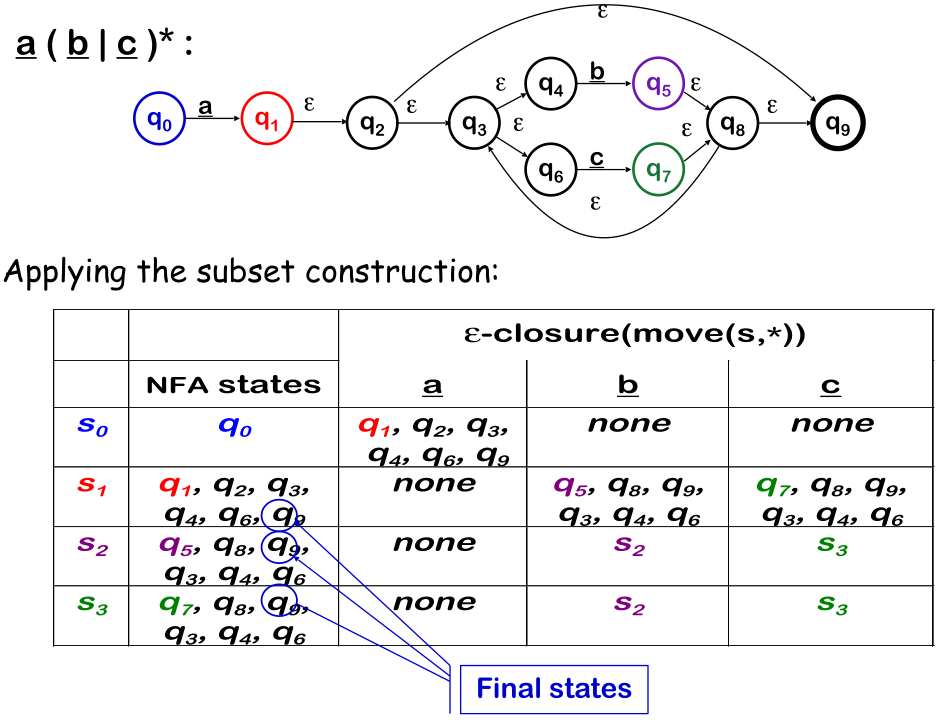
s0 = ε-closure(q0);
S.add(s0);
Worklist.add(s0);
while (!worklist.empty()) do
remove s from Wordlist;
foreach c in Σ do
t = ε-closure(move(s,c));
T[s,c] = t;
if (t ∉ S) then
S.add(t);
worklist.add(t);
end;
end;
end;
Fixed-Point Computation
- A monotone construction of some finite set (only add to the set, never remove)
- Halts when its stops adding to the set
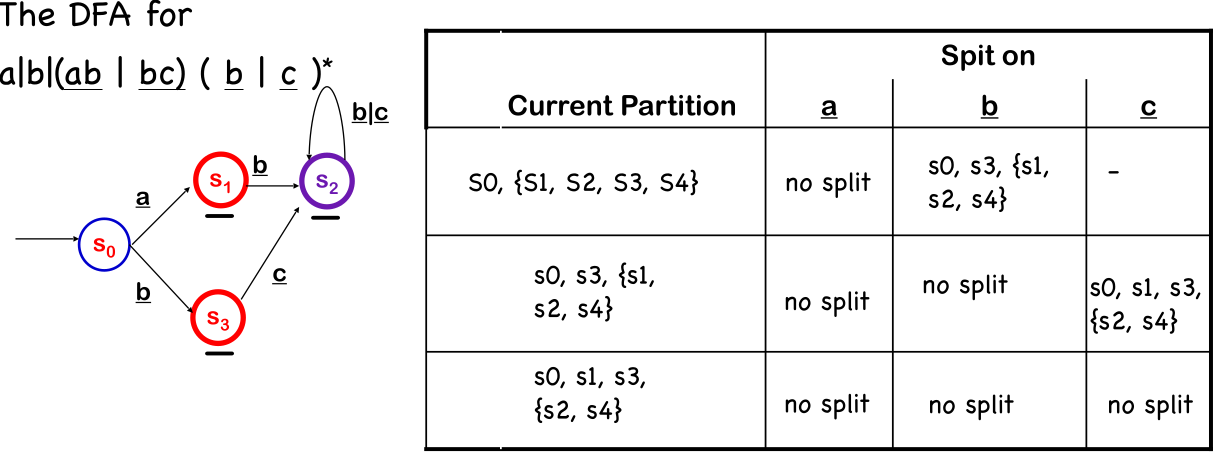
Hopcroft's Algorithm
The Hopcroft's algorithm reduces the number of states and produces a minimised DFA.
There are two sets: \(Q\) with all the "old" states, and \(P\) with all the new states.
- Put all finish states in a state and add it to \(P\) and put all non-finish states and add it to \(P\)
- Take each \(S \in P\) and repeat until \(P\) doesn't change
- Check if \(\alpha \in \Sigma\) splits \(S\) into \(S_1\) and \(S_2\). If yes, replace \(S\) with \(S_1\) and \(S_2\) in \(P\)
The following pseudo code represents the algorithm.
P = { F, {Q without F} }
while ( P is still changing)
T = {}
for each set S ∈ P
remove S from P
T = T ∪ Split(S)
P = T
Split(S)
for each α ∈ Σ
if α splits S into S1 and S2
then return {S1 , S2}
return S
The following diagram shows when a set of states is split:
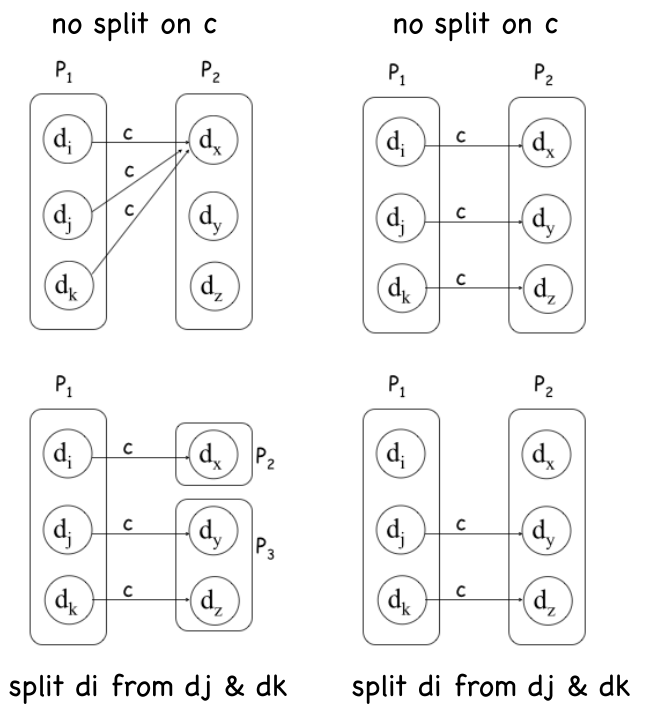
The following shows an example: