DB SCAN
DB-SCAN
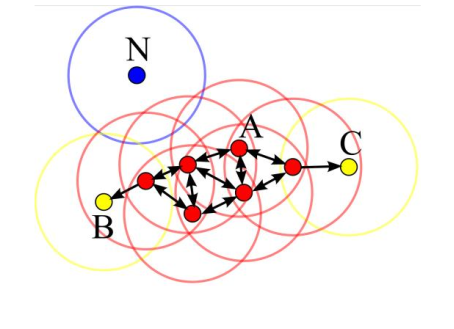
DB-SCAN categorizes each point as:
-
Core Point A point with at least \(minPts\) within the distance \(\varepsilon\) from itself
-
Border Point A point with at least one core point within the distance \(\varepsilon\) of itself
-
Noise Point A point which is neither a core point or border point
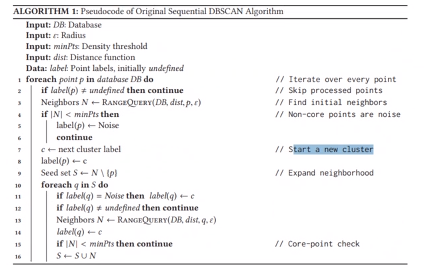
The algorithm does the following steps:
- Select an unprocessed data point \(P\) and retrieve all points within \(\varepsilon\)
- Mark \(P\) as processed
- If the amount of points found is greater or equal to \(minPts\), then
- then mark as core point
- Mark all non-core points within \(\varepsilon\) as border points (and may override noise) and assign them to the cluster of \(P\)
-
Else, if there are no core point or not \(minPts\) within \(\varepsilon\) mark it as noise
-
A smaller \(\varepsilon\) leads to more points marked as noise
- A smaller \(minPts\) leads to more clusters
The runtime complexity is \(O(m \cdot \log m)\approx O(m^2)\).
- Advantages
- No need to specify the number of cluster in advance
- Able to find arbitrarily shaped cluster
- Is able to detect noise
- Disadvantages
- Cannot cluster data sets well large differences in densities as the \(\varepsilon\) and \(minPts\) would have to change for each densitiy reagion. (An improved version, which addresses this issue, is named OPTICS)
An visualisation can be viewed at https://educlust.dbvis.de/#