3D Interaction
Interaction within the Graphics Pipeline
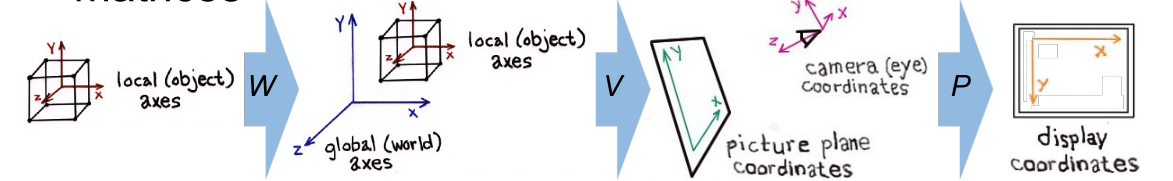
When we want to interact with something in our world, we have to reverse the graphics pipeline. There are a few ways to map the interaction in 2D into the 3D space:
- Restrict to one axis of the coordinate system (X, Y, or Z)
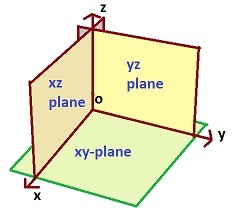
- Restrict to orthogonal planes of the coordinate system (XY, XZ, YZ, ...)
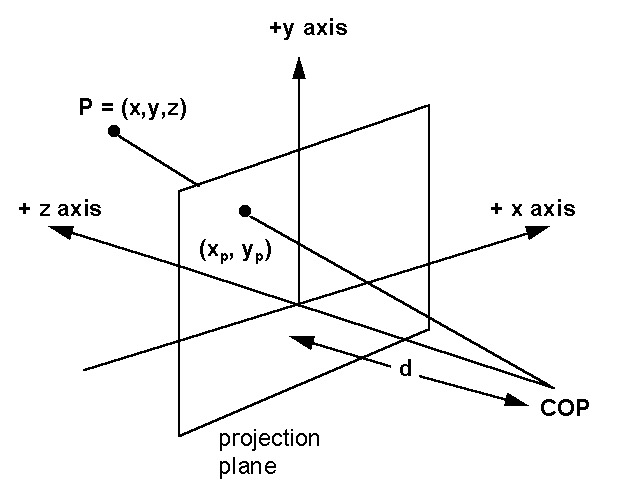
- Restrict to a projection plane of the camera
- Restrict to an axis or plane of the local object coordinate system
Euler Rotation vs Quaternions
An rotation can be decomposed into an rotation around each axis. These rotations are called Euler angles. $$ R(\theta)=R_z(\theta_z)\cdot R_y(\theta_y)\cdot R_x(\theta_x) $$
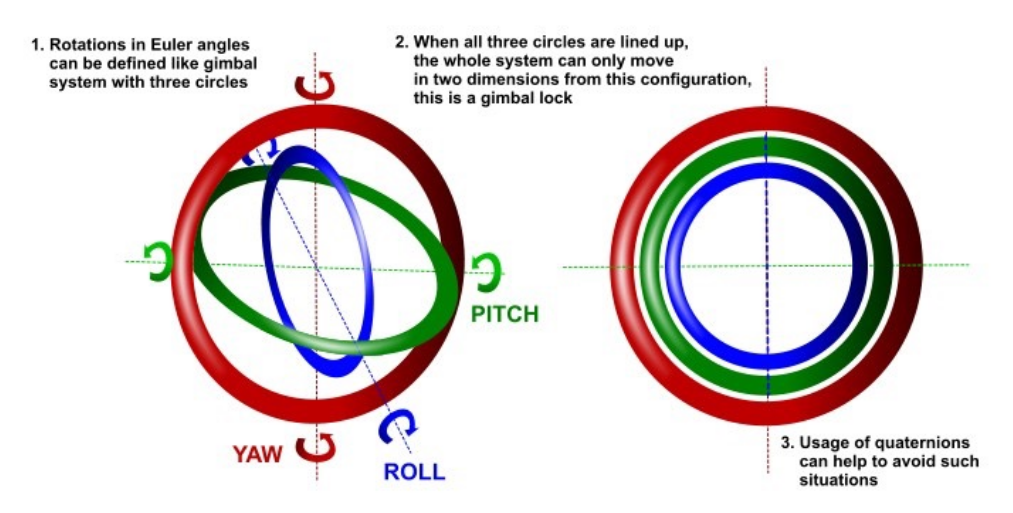
Gimble Lock
A problem with euler angles is that a gimble lock, where each rotation axis is aligned, can occurr. It's not clearly defined, how to get out of the lock.
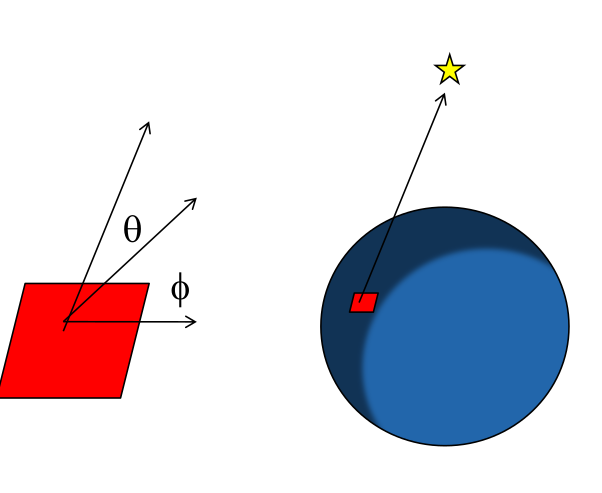
Flip Problem
The flip problem occurs when one wants to calculate the angle with which they look at the north star (or any other external point)
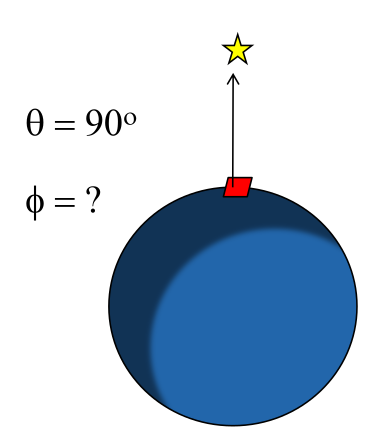
However, if one stands directly under neath the north star, what is the angle? It is not defined. This is called the flip problem.
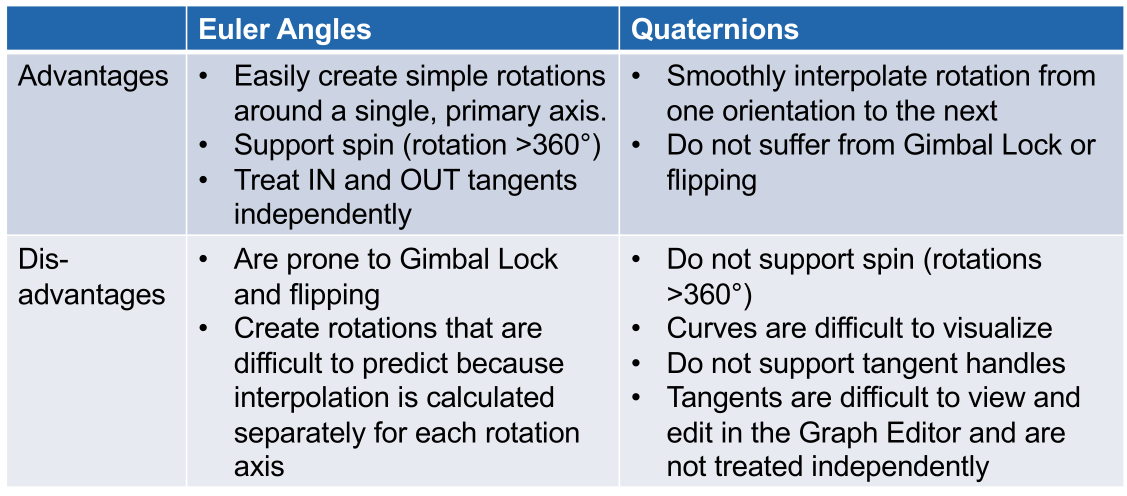
Comparison
Camera Navigation
See in VC2_02_3D_Interaction.pdf slide
Object Picking in 3D
A ray is shot from the camera through the 2D view screen into the scene.
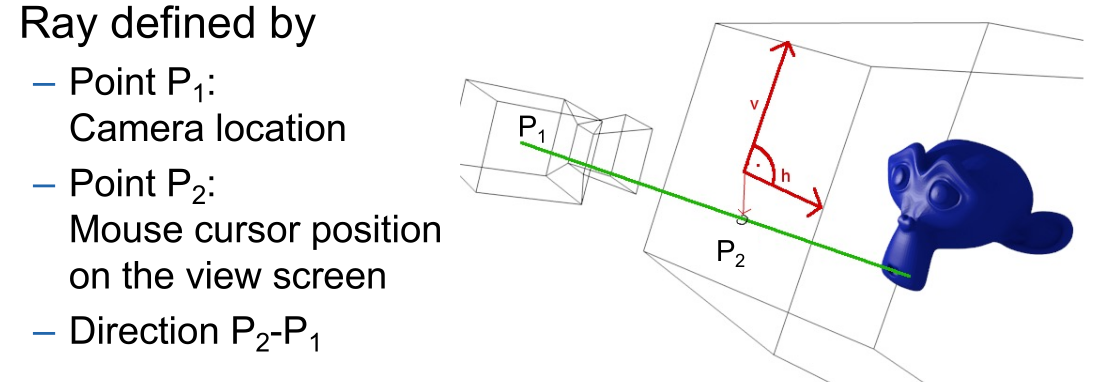
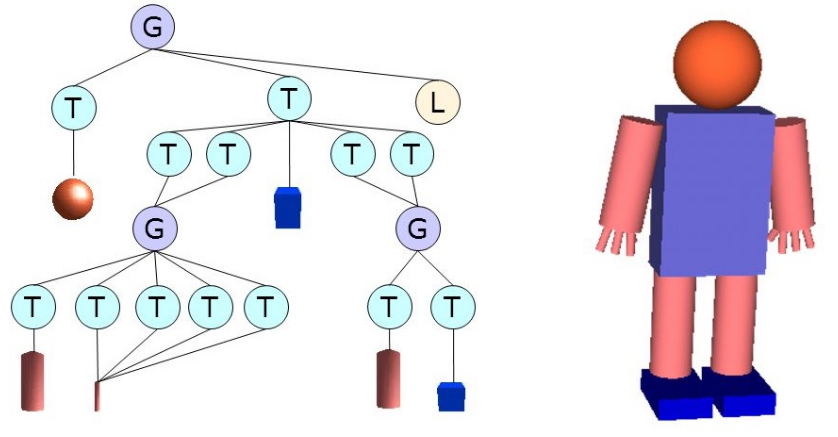
Additionally, to check if a ray hits a triangle, the ray needs to be transformed into the local coordinate system of the triangle. This can become expensive, if a large scene tree is being used. This can be some what optimised by first checking if a bounding box is hit, and only then check if the ray intersected with the polygon triangles.
This can be done as follows in THREE.js:
const projector = new THREE.Projector();
const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster();
const mouseVector = new THREE.Vector3();
mouseVector.x = (event.clientX / window.innerWidth) * 2 - 1;
mouseVector.y =-(event.clientY / window.innerHeight) * 2 + 1;
mouseVector.z = 0.5;
projector.unprojectVector(mouseVector, camera);
raycaster.set(camera.position, mouseVector.sub(camera.position).normalize());
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects(scene.children, true);
Dragging Object in 3D
When dragging an object in 3D there are multiple approaches on how to implement this:
- If the object is on the ground, clip the object to the ground and translate it on the other axes
- Translate along the x, y or z axis depending what fits best with the camera direction
- Translate the object along a temporary plane orthogonal to the viewing direction
Text in 3D
Text can be shown in different ways:
- As a label

- As a tooltip
- As UI elements