Tenses
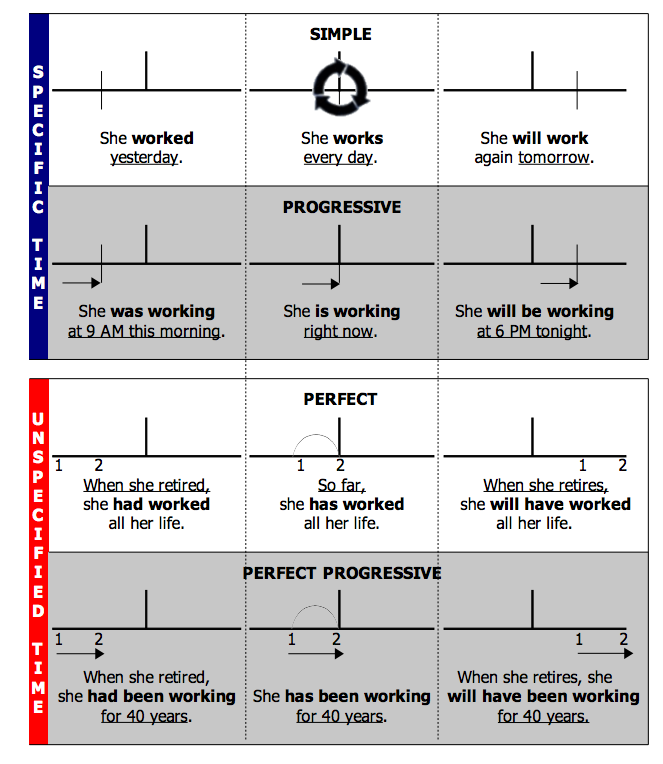
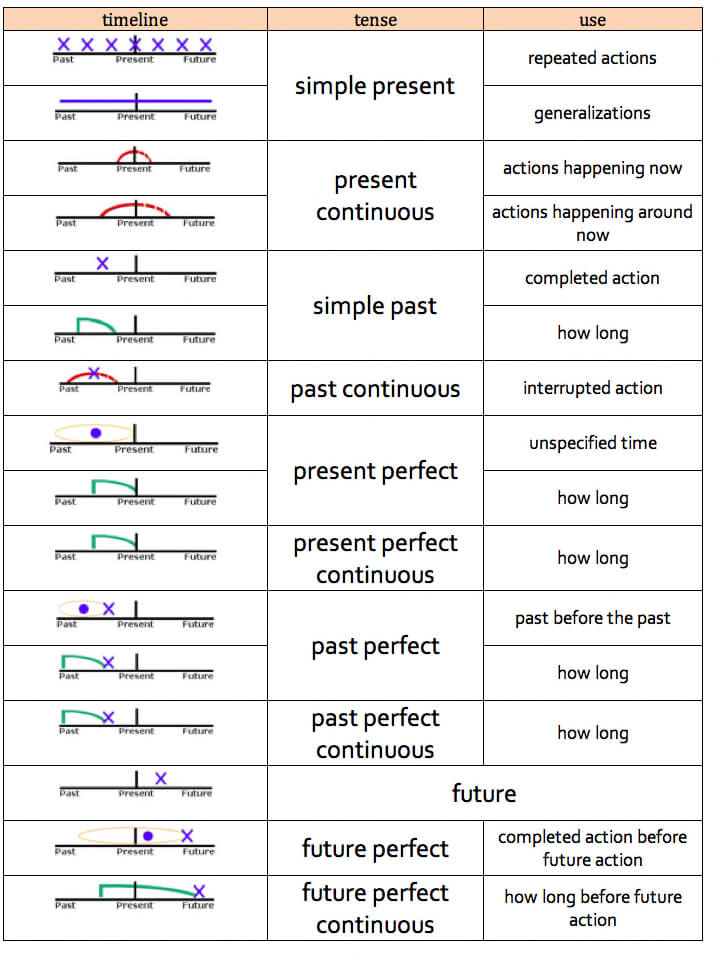
Present
Present Simple
I work everyday.
Water is wet.
My plane leaves at eight o'clock.
- Something happens repeatedly
- A generalisation
- One action follows another
- A future action which follows a timetable
Stative Verbs
Stative verbs require the present simple tense and can't be used with any continuous tense.
- thoughts and opinions: agree, belive, doubt, guess, imagine, know, mean ,recognise, remember, suspect, think, understand
- feelings and emotions: dislike, hate, like, love, prefer, want, wish
- senses and perceptions: appear, be, feel, hear, look, see, seem, smell, taste
- possession and measurement: belong, have, measure, own, possess, weigh
There are verbs which can be both stative and dynamic depending on the meaning in the context.
- be: When it's used in the continuous form, it means 'behaving' or 'acting'
you are stupid= it's part of your personalityyou are being stupid= only now, not usually- think:
I think the coffee is great= I'm of the opinion, that coffee is greatI'm thinking about my next holiday= I'm considering my next holiday- have
I have a car= I own a carI'm having a party/a good time/a bath= having is part of an expression- see
I see a house= I see something with my eyesI've been seeing my boyfriend for two years= I've been dating somebody for two yearsI'm seeing Robert tomorrow= I'm going to meet Robert tomorrow
Present Continuous
Peter is phoning his grandparents (meaning: He is doing it right now)
They are dating on Saturday (A plan, scheduled in advance)
Julie is living in Paris for a few months
- Something is happening while speaking
- Something in the future which is already scheduled
- When something is temporary
Present Perfect
I have been working (meaning: I started working earlier and stopped now)
I've cleaned my room. (meainig: I cleaned my room and the result, the clean room, is now relevant)
I just played football.
We have lived in Canada since 2012. (Has an connection to the present, as "we" are still living there)
- An action which started in the past and continues up to the present
- A recently completed action
- Am action in the past which has a connection to the present
- An experience you had in the past but doesn't have to be recent
Signal words: just, already, up to now, until now / till now, ever, (not) yet, so far, lately / recently
Present Perfect Continuous
She has been writing for to hours. (Puts emphasis on the duration or course of action, but not on the result)
I have been living here since 2001. (Action that recently stopped or is still going on)
I have been working all afternoon. (finished action which influenced the present)
Why are you so wet? - I've been washing my car.
- Emphasises the length of time of an recently stopped action or an action which is still going on
- How long an action has been happening
- A unwanted side effect
Link Simple vs Continuous: https://www.ego4u.com/en/cram-up/grammar/prepersim-preperpro
Signal words: how long since, for
Present Perfect
Past
Past Simple
I worked (meaning: I started and stopped working in the past)
When I was having breakfast, the phone suddenly rang.
- An action which finished in the past and isn't connected to the present
- An action in the past which takes place in the middle of another action
- Signal Words:
- A time expression in the past
Past Continuous
While I was working, I met a child hood friend.
Kim was helping my parents moving today in the morning. (meaning: Kim was helping and might still be helping, but the speaker doesn't know)
While she was preparing dinner, he was washing the dishes.
- An action in the middle of another action (often with
while) - An action which started in the past at a certain time, but the speaker doesn't know if it was finished or not
- Two simultaneously actions in the past
Past Perfect Simple
Mary had read the book before she watched the film.
If I had seen him, I would have talked to him (conditional sentence III)
- When an action (past perfect) which has already happened, is followed by another action
- Conditional Sentences Type III
Signal words: already, just never, not yet, once, until that day
Past Perfect Continuous
He had been talking for two hours straight when the bell finally rang.
- Puts emphasis on the course or duration of an action taking place before a certain time in the past
- But like the past perfect simple, it is used when talking about an action before another action
Future
In the case the an action was scheduled, a sentence can be formed with the present continuous or the going to (I'm having a party. \(\a\) I'm going to have a party.)
Will-Future
It will rain later. (A prediction made by the speaker)
I will bet on red (meaning: I decided while speaking that I will bet on read)
If I study, I will pass the exams
- A prediction about the future
- When saying somthing about the future, which is almost certain
- When a decision was spontaneously made at the time of speaking
- The main clause in the type 1 if-clause
Future Continuous
When I come to school, the other kids will be waiting for me
- An action which will be in progress at a certain time in the future (eg. when I come to school)
Going To-Future
Mary and I are going to see a movie.
- When the speaker already decided to to an action in the future
- What the speaker thinks will happen