OpenGL
Instead of glVertex2i, the any combination of glVertex[234][isfd] could have been used, where [234] stands for 2D, 3D and 4D and [isfd] stands for integer, short, float and double.
To draw a red line, the following code is necessary:
glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,0.0); // Background color
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); // Set transformation
glLoadIdentity(); // Load trans. matrix
gluOrtho2D(0, 200, 0, 150); // Set cam projection
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear background
glColor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); // Set color to red
glBegin(GL_LINES); // Draw line
glVertex2i(180, 15); // - first point
glVertex2i(10, 145); // - second point
glEnd(); // Ready with line
glFlush(); // Send
Setting attributes can change how primitives are drawn (e.g. color, width, style, etc). The current value is always maintaned and it can be changed with a function. Some attributes need to be enabled with glEnable(...).
For example, the following draws a line with the attribute GL_LINE_STIPPLE enabled:
glLineWidth(2);
glEnable(GL_LINE_STIPPLE);
glLineStipple(repeatfactor, pattern);
// draw stippled lines
...
glDisable(GL_LINE_STIPPLE);
OpenGL Primitives
| Name | Example |
|---|---|
GL_POINTS |
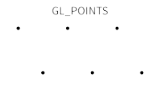 |
GL_LINES |
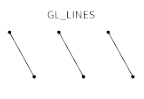 |
GL_LINE_STRIP |
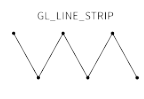 |
GL_LINE_LOOP |
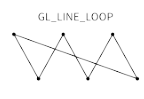 |
GL_TRIANGLES |
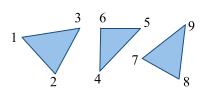 |
GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP |
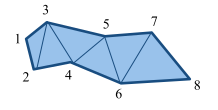 |
GL_POLYGON |
 |
GL_TRIANGLE_FAN |
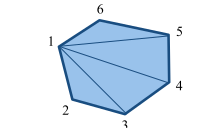 |
GL_QUADS |
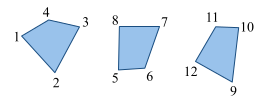 |
GL_QUADS_STRIP |
 |
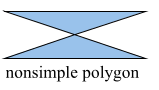
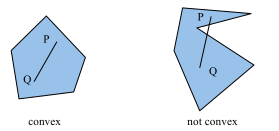
OpenGL can only draw polygons that are simple, convex and flat:
- simple: edges cannot cross
- convex:
- flat: all vertices must be in the same plane
Efficiency
To reduce the number of functions, vertices can be passed as an array
There are also techniques to send data to the GPU once and store it there. Display lists are collections of OpenGL commands which can be referenced later. This is useful for static geometries/scenes. In modern OpenGL this concept is called Vertex Buffer Object.
GL, GLU, GLUT
- GL: OpenGL functions
- GLU: OpenGL Utility library
- GLUT: OpenGL Utility Toolkit library (very old)
Examples
// === Setup Viewing Transformation ===
glViewport(0, 0, 500, 500); // Select part of window
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);// Set projection matrix
glLoadIdentity(); // Load identity matrix
glFrustum(-1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0, 4.0, 20.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); // Set camera matrix
glLoadIdentity();
gluLookAt(3.0, 6.0, 5.0, // - eye point
1.0, 0.0, 0.0, // - center point
0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // - up axis
// === Set Window Background Color & Drawing Color ===
// Clear background
glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,0.0);// Background color
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear background
// Set drawing color
glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
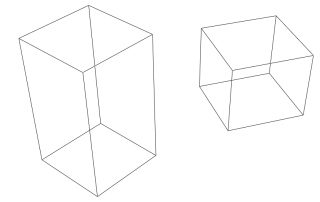
// === Draw geometry ===
// Draw two rectangular boxes
glutWireCube(1.0);
// unit box around origin
glTranslatef(2.0, 0.0, 0.0); // move in x-direction
glRotatef(30.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // rotate 30 degrees
// around z-axis
glScalef(1.0, 1.0, 2.0);
// scale in z-direction
glutWireCube(1.0); // translated, rotated, scaled box
PyOpenGL Example
The code below produces the following spinning rectangle:
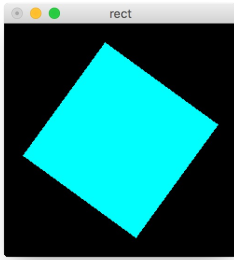
spin = 0.0
def display():
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)
glPushMatrix()
glRotatef(spin, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
glColor3f(0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
glRectf(-3.0, -3.0, 3.0, 3.0)
glPopMatrix()
glutSwapBuffers()
def spinDisplay():
global spin
spin = spin + 2.0
if (spin > 360.0):
spin = spin - 360.0
glutPostRedisplay()
def init():
glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
glShadeModel(GL_FLAT)
def reshape(w, h):
glViewport(0, 0, w, h)
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION)
glLoadIdentity()
glOrtho(-5.0, 5.0, -5.0, 5.0, -1.0, 1.0)
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)
glLoadIdentity()
OBJ File Format
Simple format used to store geometry. Its content is encoded in ASCII.
vstores a vertex on the linevnstores the normal vertexvtstores texture coordinatesfCreates a face from the given indices specified in the formatvertex//normal