Resources
Cgroups can be used to organise tasks into groups whose usage of various types of resources can then be strictly controlled.
To control cgroups, one creates a tempfs (optionally), creates a directory in it and mounts a resource control interface into that directory. Magically, configuration file associated with the resource type appear in the config directory. Later a PID needs to be associated with a controll configuration.
Termonology
- Cgroup A collection of processes that are bound to a set of limits
- Subsystem/Resource Controllers A kernel component related to a resource type
- Hierarchy Controllers are arranged in a hierarchy. A process cannot exceed the limits placed by the related cgroup and all its parent cgroups. Cgroups higher in the hierarchy means that less restrictions are placed up on it.
Setup Up
-
Create a temp file system
sudo mount -t tmpfs -o size=10M tmpfs /mnt/mytmpfs -
Mount the resource control interface in the tempfs
mount -t cgroup -o cpu,cpuacct none /mnt/mytempfs/cpu,cpuacct -
A new cgroup can be created by creating a directory
mkdir /mnt/mytempfs/cpu/cg1
-
To associate a PID with a cgroup, it needs to be appended
echo $$ > /mnt/mytempfs/cpu/cg1/cgroup.procs -
To remove the configuration, unmount the tmpfs
umount /mnt/mytempfs/
Limitations
A controller can only be associated with one directory structure.
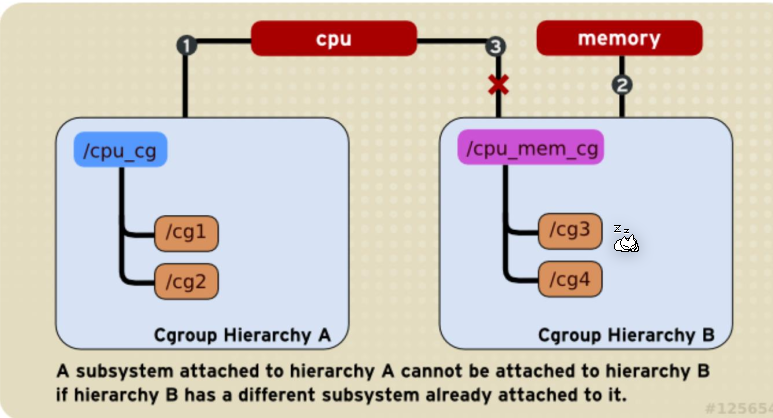
A processes cannot be associated with two cgroups on the same hierarchy for the same controller.
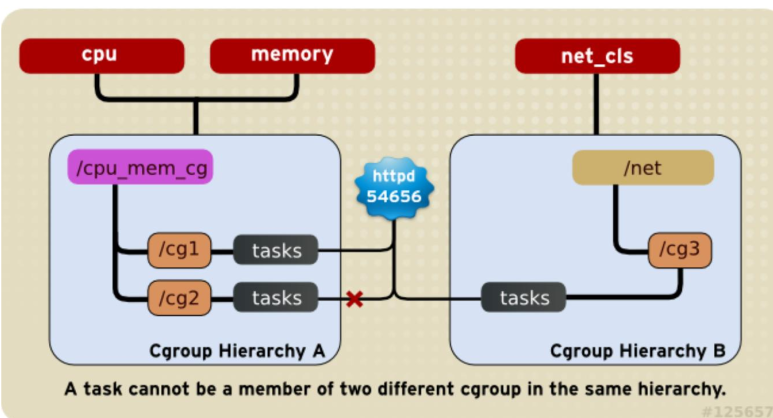
Controllers
Usually, an lower limit can be configured to guarantee an amount of resource and an upper limit to limit the amount of resource.
- CPU The time share
- Cpuset A specific set of cpus
- Memory The process memory, kernel memory and swap used
-
Blkio (block-io device)
Example
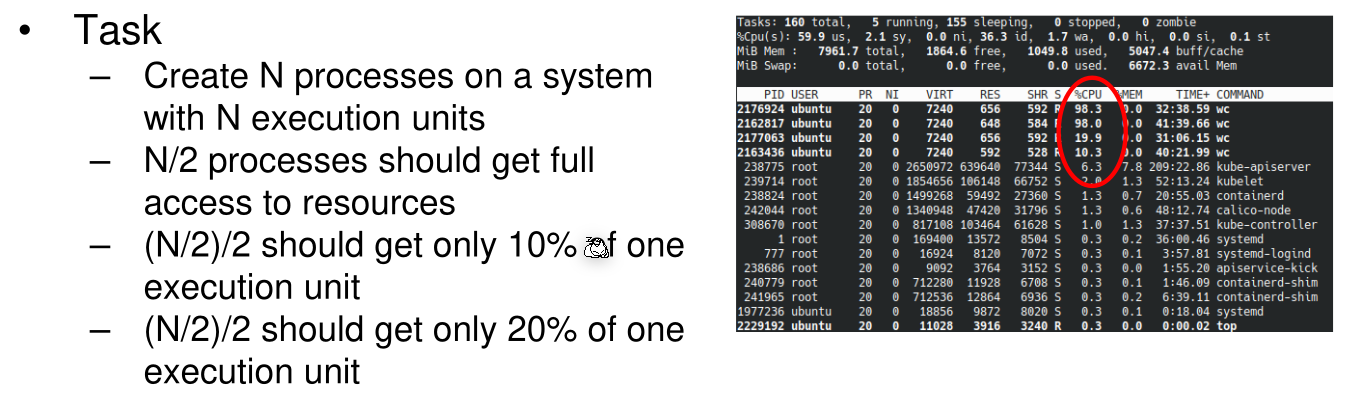
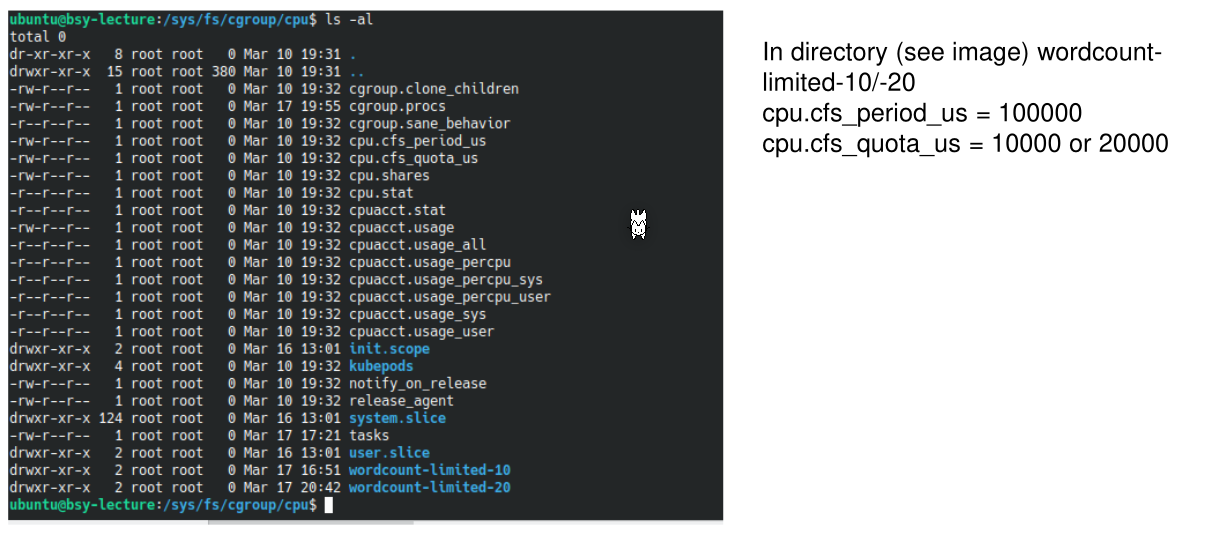
100'000 was written into cpu.cfs_period_us and cpu.cfs_quota_us to 10'000 and 20'000 respectively.
The following steps is an example to deny the access to the device /dev/null. echo 0 > sys/fs/cgroup/devices/group0/tasks will deny access for the current process, in this case the current shell.
